Test in production without watermarks.
Works wherever you need it to.
Get 30 days of fully functional product.
Have it up and running in minutes.
Full access to our support engineering team during your product trial
In the realm of Java programming, efficient string manipulation is a cornerstone skill. The ability to parse, split, and manipulate strings is essential for various tasks, ranging from data processing to text parsing. One fundamental method for splitting strings in Java is the split() method.
In this article, we'll delve into the intricacies of the Java Split Pipe method, focusing particularly on its usage with the pipe (|) separator. Also, we will create a PDF file using IronPDF for Java using Java Split Pipe delimited string splitting.
The split() method is a convenient tool provided by Java's String class, enabling developers to split a string into an array of substrings based on a specified delimiter. Its signature is as follows:
public String[] split(String regex)Here, regex is a regular expression that defines the delimiter used for splitting the string. Regular expressions offer a powerful way to specify patterns for text matching and manipulation.
The pipe (|) character serves as an alternate delimiter in various contexts, including regular expressions. In Java, the pipe symbol is treated as a metacharacter within regular expressions and denotes the logical OR operation. When used within the split() method, the pipe character serves as a delimiter, splitting string wherever it occurs.
Let's start with a basic example to illustrate the usage of the pipe separator with the split() method:
public class SplitExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String text = "apple|banana|orange|grape";
String[] fruits = text.split("\\|");
for (String fruit : fruits) {
System.out.println(fruit);
}
}
}In this example, the string "apple|banana|orange|grape" is split into an array of substrings using the pipe character (|) as the delimiter. The double backslash (\) is used to escape the pipe character because it is a metacharacter in regular expressions.
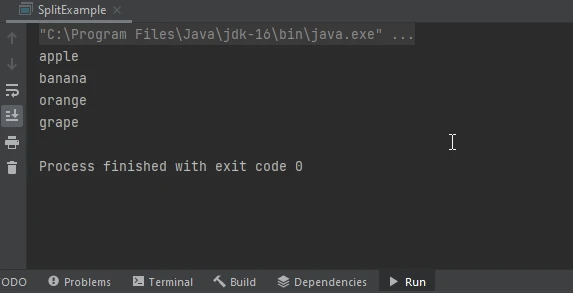
When using special characters such as the pipe symbol as delimiters, it's crucial to handle them properly to avoid unexpected behavior. Since the pipe symbol has a specific meaning in regular expressions, it needs to be escaped to be treated as a literal character. This is achieved by preceding it with a backslash (\), as shown in the previous example.
One of the strengths of the split() method is its ability to split a string based on multiple delimiters. This is achieved by constructing a regular expression that represents a logical OR between the delimiters. For example:
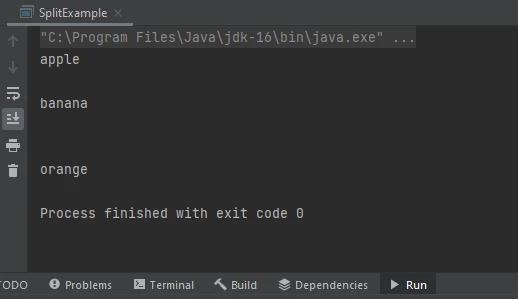
String text = "apple,banana;orange|grape";
String[] fruits = text.split("[,;\\|]");In this example, the string "apple,banana;orange|grape" is split using a regular expression that matches commas (,), semicolons (;), and pipe characters (|).
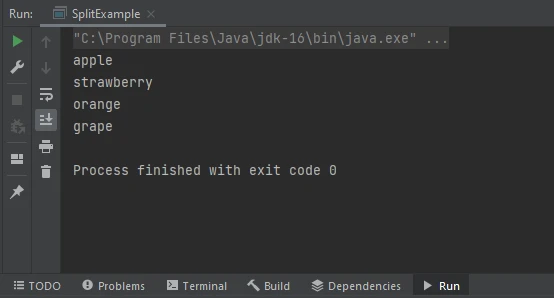
By default, the split() method discards empty strings that result from consecutive delimiters. However, there are scenarios where preserving empty strings is desirable. To achieve this, we can specify a negative limit as the second argument to the split() method. For example:
String text = "apple||banana|||orange";
String[] fruits = text.split("\\|", -1);In this example, the pipe character (|) is used as the delimiter, and a negative limit is specified to preserve empty strings. As a result, the array fruits will contain elements for all occurrences of the delimiter, including consecutive ones.
IronPDF for Java is a powerful library that enables developers to create, manipulate, and render PDF documents within their Java applications. It provides an intuitive API that abstracts away the complexities of PDF generation, allowing developers to focus on building their applications rather than dealing with low-level PDF manipulation tasks.
In the realm of software development, generating PDF documents programmatically is a common requirement. Whether it's generating reports, invoices, or certificates, having a reliable tool to create PDFs dynamically is crucial. One such tool that simplifies PDF generation for Java developers is IronPDF.
To set up IronPDF, ensure you have a reliable Java Compiler. In this tutorial, we'll utilize IntelliJ IDEA.
Once the project is created, access the Pom.XML file. Insert the following Maven dependencies to integrate IronPDF:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.ironsoftware</groupId>
<artifactId>com.ironsoftware</artifactId>
<version>2024.3.1</version>
</dependency>import com.ironsoftware.ironpdf.*;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
// Apply your license key
License.setLicenseKey("YOUR-LICENSE-KEY");
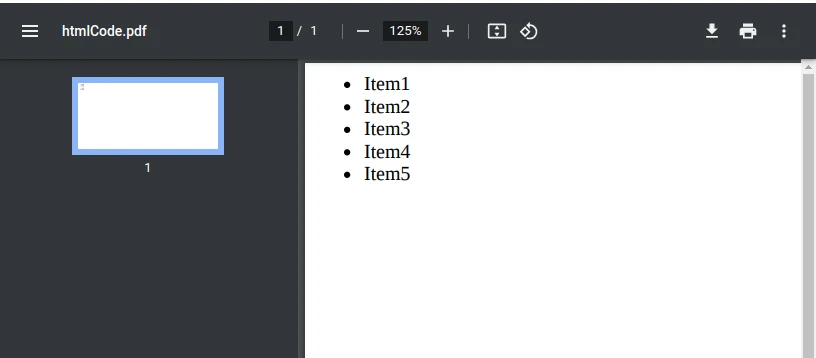
String data = "Item1|Item2|Item3|Item4|Item5";
// Split data into a list
String[] items = data.split("\\|");
// Create HTML list
StringBuilder htmlList = new StringBuilder("<ul>\n");
for (String item : items) {
htmlList.append(" <li>").append(item).append("</li>\n");
}
htmlList.append("</ul>");
PdfDocument myPdf = PdfDocument.renderHtmlAsPdf(htmlList.toString());
// Save the PdfDocument to a file
myPdf.saveAs(Paths.get("htmlCode.pdf"));This code snippet demonstrates how to generate a PDF document from an HTML-formatted string. First, it imports the necessary libraries for PDF generation and file operations. Then, it sets a license key for IronPDF, a library used for PDF operations.
A string data is defined with pipe-separated values. The string is split into a string array called items using the pipe character as a delimiter.
Next, an HTML list (htmlList) is constructed by appending each item from the items array into list item () tags within an unordered list ().
The PdfDocument.renderHtmlAsPdf() method converts this HTML string into a PDF document, which is then saved as "htmlCode.pdf" using the saveAs() method.
In summary, the code takes a string of data, formats it as an HTML list, converts that HTML to a PDF using IronPDF, and saves the resulting PDF as "htmlCode.pdf".
In this comprehensive overview of Java's string manipulation and PDF generation capabilities, we explored the split() method's functionality, particularly its use with the pipe (|) delimiter. The split() method provides a versatile way to break down strings into substrings based on specified delimiters, including handling special characters and multiple delimiters. IronPDF emerged as a powerful tool for dynamically generating PDF documents in Java, simplifying the process by abstracting low-level PDF manipulation.
The provided example illustrated how to leverage Java's string splitting capabilities alongside IronPDF to transform an HTML-formatted string into a PDF document, showcasing the seamless integration of string manipulation and PDF generation in Java.
As software development frequently requires generating PDFs for reports, invoices, and more, mastering these techniques equips developers with essential skills to handle such tasks efficiently.
To know more about IronPDF functionality, visit the IronPDF Documentation Page to see how IronPDF could help with your projects today. IronPDF Licensing Information starts at $749 USD.