Test in production without watermarks.
Works wherever you need it to.
Get 30 days of fully functional product.
Have it up and running in minutes.
Full access to our support engineering team during your product trial
DateTime objects in C# are fundamental for working with dates and times in .NET Framework applications. They provide a robust set of functionalities for manipulating, formatting, and comparing dates and times.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of DateTime objects in C#, covering their creation, manipulation, formatting, and common use cases. At the end of the article, we will also explore how IronPDF from Iron Software can generate a PDF document on the fly in C# applications.
Creating a DateTime object in C# is straightforward. There are several constructors available to initialize a DateTime object with different parameters:
// Current date and time
DateTime currentDateTime = DateTime.Now;
// Specific date and time
DateTime specificDateTime = new DateTime(2024, 3, 16, 10, 30, 0);
// Date only
DateTime dateOnly = DateTime.Today;
// Date and time in UTC
DateTime utcDateTime = DateTime.UtcNow;// Current date and time
DateTime currentDateTime = DateTime.Now;
// Specific date and time
DateTime specificDateTime = new DateTime(2024, 3, 16, 10, 30, 0);
// Date only
DateTime dateOnly = DateTime.Today;
// Date and time in UTC
DateTime utcDateTime = DateTime.UtcNow;' Current date and time
Dim currentDateTime As DateTime = DateTime.Now
' Specific date and time
Dim specificDateTime As New DateTime(2024, 3, 16, 10, 30, 0)
' Date only
Dim dateOnly As DateTime = DateTime.Today
' Date and time in UTC
Dim utcDateTime As DateTime = DateTime.UtcNowDateTime ObjectsDateTime objects provide various methods for manipulating dates and times, such as adding or subtracting time intervals, extracting components, and converting between time zones.
DateTime now = DateTime.Now;
// Adding days
DateTime futureDate = now.AddDays(7);
// Subtracting hours
DateTime pastTime = now.AddHours(-3);
// Getting components
int year = now.Year;
int month = now.Month;
int day = now.Day;
int hour = now.Hour;
int minute = now.Minute;
int second = now.Second;
// Converting between time zones
DateTime utcTime = DateTime.UtcNow;
DateTime localTime = utcTime.ToLocalTime();DateTime now = DateTime.Now;
// Adding days
DateTime futureDate = now.AddDays(7);
// Subtracting hours
DateTime pastTime = now.AddHours(-3);
// Getting components
int year = now.Year;
int month = now.Month;
int day = now.Day;
int hour = now.Hour;
int minute = now.Minute;
int second = now.Second;
// Converting between time zones
DateTime utcTime = DateTime.UtcNow;
DateTime localTime = utcTime.ToLocalTime();Dim now As DateTime = DateTime.Now
' Adding days
Dim futureDate As DateTime = now.AddDays(7)
' Subtracting hours
Dim pastTime As DateTime = now.AddHours(-3)
' Getting components
Dim year As Integer = now.Year
Dim month As Integer = now.Month
Dim day As Integer = now.Day
Dim hour As Integer = now.Hour
Dim minute As Integer = now.Minute
Dim second As Integer = now.Second
' Converting between time zones
Dim utcTime As DateTime = DateTime.UtcNow
Dim localTime As DateTime = utcTime.ToLocalTime()DateTime ObjectsDateTime objects represent times or dates that can be formatted into strings using various format specifiers to represent them in the required format.
DateTime dateTime = DateTime.Now;
// Standard date and time format
string standardFormat = dateTime.ToString("G");
// Custom format
string customFormat = dateTime.ToString("dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm:ss");
// Format for sorting
string sortableFormat = dateTime.ToString("yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss");DateTime dateTime = DateTime.Now;
// Standard date and time format
string standardFormat = dateTime.ToString("G");
// Custom format
string customFormat = dateTime.ToString("dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm:ss");
// Format for sorting
string sortableFormat = dateTime.ToString("yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss");Imports System
Dim dateTime As DateTime = DateTime.Now
' Standard date and time format
Dim standardFormat As String = dateTime.ToString("G")
' Custom format
Dim customFormat As String = dateTime.ToString("dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm:ss")
' Format for sorting
Dim sortableFormat As String = dateTime.ToString("yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss")DateTime ObjectsC# provides standard comparison operators (<, >, <=, >=, ==, !=) that can be used to compare two DateTime objects directly. These operators compare the underlying ticks of the DateTime objects, which represent the number of 100-nanosecond intervals that have elapsed since January 1, 0001, at 00:00:00.000 in the Gregorian calendar.
Here's an example demonstrating the use of comparison operators:
DateTime date1 = DateTime.Now;
DateTime date2 = DateTime.Now.AddDays(1);
if (date1 < date2)
{
Console.WriteLine("date1 is earlier than date2.");
}
else if (date1 > date2)
{
Console.WriteLine("date1 is later than date2.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("date1 is equal to date2.");
}DateTime date1 = DateTime.Now;
DateTime date2 = DateTime.Now.AddDays(1);
if (date1 < date2)
{
Console.WriteLine("date1 is earlier than date2.");
}
else if (date1 > date2)
{
Console.WriteLine("date1 is later than date2.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("date1 is equal to date2.");
}Dim date1 As DateTime = DateTime.Now
Dim date2 As DateTime = DateTime.Now.AddDays(1)
If date1 < date2 Then
Console.WriteLine("date1 is earlier than date2.")
ElseIf date1 > date2 Then
Console.WriteLine("date1 is later than date2.")
Else
Console.WriteLine("date1 is equal to date2.")
End IfDateTime.Compare C# MethodIn addition to comparison operators, DateTime objects also provide methods for comparison of the relative values between those objects. These methods offer more flexibility and readability in certain scenarios. The CompareTo() method compares the underlying DateTime objects to determine the result.
It assumes that the two dates are in the same time zone values. After comparing the objects it returns an integer value indicating greater, lesser, or equal. Same date values return an integer value of zero.
DateTime date1 = DateTime.Now;
DateTime date2 = DateTime.Now.AddDays(1);
int result = date1.CompareTo(date2);
if (result < 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("date1 is earlier than date2.");
}
else if (result > 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("date1 is later than date2.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("date1 is equal to date2.");
}DateTime date1 = DateTime.Now;
DateTime date2 = DateTime.Now.AddDays(1);
int result = date1.CompareTo(date2);
if (result < 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("date1 is earlier than date2.");
}
else if (result > 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("date1 is later than date2.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("date1 is equal to date2.");
}Dim date1 As DateTime = DateTime.Now
Dim date2 As DateTime = DateTime.Now.AddDays(1)
Dim result As Integer = date1.CompareTo(date2)
If result < 0 Then
Console.WriteLine("date1 is earlier than date2.")
ElseIf result > 0 Then
Console.WriteLine("date1 is later than date2.")
Else
Console.WriteLine("date1 is equal to date2.")
End IfDateTime Objects with ToleranceTo compare DateTime objects, especially when dealing with calculations involving time intervals, it's important to consider a tolerance level due to potential differences in precision.
This can be achieved by comparing the absolute difference between two DateTime values against a predefined tolerance threshold.
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
DateTime date1 = DateTime.Now;
DateTime date2 = DateTime.Now.AddMilliseconds(10);
TimeSpan tolerance = TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(5);
bool isEqual = Math.Abs((date1 - date2).TotalMilliseconds) <= tolerance.TotalMilliseconds;
if (isEqual)
{
Console.WriteLine("date1 is considered equal to date2 within the tolerance.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("date1 is not equal to date2 within the tolerance.");
}
}
}class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
DateTime date1 = DateTime.Now;
DateTime date2 = DateTime.Now.AddMilliseconds(10);
TimeSpan tolerance = TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(5);
bool isEqual = Math.Abs((date1 - date2).TotalMilliseconds) <= tolerance.TotalMilliseconds;
if (isEqual)
{
Console.WriteLine("date1 is considered equal to date2 within the tolerance.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("date1 is not equal to date2 within the tolerance.");
}
}
}Friend Class Program
Public Shared Sub Main()
Dim date1 As DateTime = DateTime.Now
Dim date2 As DateTime = DateTime.Now.AddMilliseconds(10)
Dim tolerance As TimeSpan = TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(5)
Dim isEqual As Boolean = Math.Abs((date1.Subtract(date2)).TotalMilliseconds) <= tolerance.TotalMilliseconds
If isEqual Then
Console.WriteLine("date1 is considered equal to date2 within the tolerance.")
Else
Console.WriteLine("date1 is not equal to date2 within the tolerance.")
End If
End Sub
End ClassDateTime objects in C# can represent both local time and Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). It's important to be aware of time zone conversions, especially when dealing with global applications.
DateTime localTime = DateTime.Now;
DateTime utcTime = DateTime.UtcNow;
Console.WriteLine("Local Time: " + localTime);
Console.WriteLine("UTC Time: " + utcTime);DateTime localTime = DateTime.Now;
DateTime utcTime = DateTime.UtcNow;
Console.WriteLine("Local Time: " + localTime);
Console.WriteLine("UTC Time: " + utcTime);Dim localTime As DateTime = DateTime.Now
Dim utcTime As DateTime = DateTime.UtcNow
Console.WriteLine("Local Time: " & localTime)
Console.WriteLine("UTC Time: " & utcTime)IronPDF from Iron Software is an efficient and easy-to-use PDF generation library. We can install it using the NuGet Package manager
NuGet\Install-Package IronPdf -Version 2024.3.4Or from Visual Studio as shown below
Now let's dive into PDF generation to demo a DateTime object.
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("-----------Iron Software-------------");
var renderer = new ChromePdfRenderer(); // var pattern
var content = " <h1> Iron Software is Awesome </h1> Made with IronPDF!";
content += "<h2>Demo Datetime Objects in C#</h2>";
// Current date and time
content += "<h3>Current date and time</h3>";
DateTime currentDateTime = DateTime.Now;
content += $"<p>Current date and time: {currentDateTime:U}</p>";
Console.WriteLine($"Current date and time: {currentDateTime:U}");
// Specific date and time
content += "<h3>Specific date and time</h3>";
DateTime specificDateTime = new DateTime(2024, 3, 16, 10, 30, 0);
content += $"<p>Specific date and time: {specificDateTime:U}</p>";
Console.WriteLine($"Specific date and time: {specificDateTime:U}");
// Date only
content += "<h3>Date Only</h3>";
DateTime dateOnly = DateTime.Today;
content += $"<p>Date only: {dateOnly:U}</p>";
Console.WriteLine($"Date only: {dateOnly:U}");
// Date and time in UTC
content += "<h3>Date and time in UTC</h3>";
DateTime utcDateTime = DateTime.UtcNow;
content += $"<p>Date only: {dateOnly:U}</p>";
Console.WriteLine($"Date only: {dateOnly:U}");
//Compare dates with Operators
content += "<h3>Compare dates with Operators</h3>";
DateTime date1 = DateTime.Now;
DateTime date2 = DateTime.Now.AddDays(1);
content += $"<p>Compare date1 {date1:d}, date2 {date2:d}: {CompareDates(date1, date2)}</p>";
Console.WriteLine($"Compare date1 {date1:U}, date2 {date2:U}: {dateOnly:U}");
//Compare dates with Compare Method
content += "<h3>Compare dates with Compare Method</h3>";
content += $"<p>Compare date1 {date1:d}, date2 {date2:d}: {CompareDatesWithCompare(date1, date2)}</p>";
Console.WriteLine($"Compare date1 {date1:U}, date2 {date2:U}: {dateOnly:U}");
var pdf = renderer.RenderHtmlAsPdf(content);
pdf.SaveAs("outputDate.pdf"); // Saves PDF
}
public static string CompareDatesWithCompare(DateTime date1, DateTime date2)
{
int result = date1.CompareTo(date2);
string resultString;
if (result < 0)
{
resultString = "date1 is earlier than date2.";
Console.WriteLine(resultString);
}
else if (result > 0)
{
resultString = "date1 is later than date2.";
Console.WriteLine(resultString);
}
else
{
resultString = "date1 is equal to date2.";
Console.WriteLine(resultString);
}
return resultString;
}
public static string CompareDates(DateTime date1, DateTime date2)
{
string result;
if (CheckLessor(date1, date2))
{
result = "date1 is earlier than date2.";
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
else if (CheckGreater(date1, date2))
{
result = "date1 is later than date2.";
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
else
{
result = "date1 is equal to date2.";
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
return result;
}
public static bool CheckGreater(DateTime date1, DateTime date2)
{
return date1 > date2;
}
public static bool CheckLessor(DateTime date1, DateTime date2)
{
return date1 < date2;
}
}class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("-----------Iron Software-------------");
var renderer = new ChromePdfRenderer(); // var pattern
var content = " <h1> Iron Software is Awesome </h1> Made with IronPDF!";
content += "<h2>Demo Datetime Objects in C#</h2>";
// Current date and time
content += "<h3>Current date and time</h3>";
DateTime currentDateTime = DateTime.Now;
content += $"<p>Current date and time: {currentDateTime:U}</p>";
Console.WriteLine($"Current date and time: {currentDateTime:U}");
// Specific date and time
content += "<h3>Specific date and time</h3>";
DateTime specificDateTime = new DateTime(2024, 3, 16, 10, 30, 0);
content += $"<p>Specific date and time: {specificDateTime:U}</p>";
Console.WriteLine($"Specific date and time: {specificDateTime:U}");
// Date only
content += "<h3>Date Only</h3>";
DateTime dateOnly = DateTime.Today;
content += $"<p>Date only: {dateOnly:U}</p>";
Console.WriteLine($"Date only: {dateOnly:U}");
// Date and time in UTC
content += "<h3>Date and time in UTC</h3>";
DateTime utcDateTime = DateTime.UtcNow;
content += $"<p>Date only: {dateOnly:U}</p>";
Console.WriteLine($"Date only: {dateOnly:U}");
//Compare dates with Operators
content += "<h3>Compare dates with Operators</h3>";
DateTime date1 = DateTime.Now;
DateTime date2 = DateTime.Now.AddDays(1);
content += $"<p>Compare date1 {date1:d}, date2 {date2:d}: {CompareDates(date1, date2)}</p>";
Console.WriteLine($"Compare date1 {date1:U}, date2 {date2:U}: {dateOnly:U}");
//Compare dates with Compare Method
content += "<h3>Compare dates with Compare Method</h3>";
content += $"<p>Compare date1 {date1:d}, date2 {date2:d}: {CompareDatesWithCompare(date1, date2)}</p>";
Console.WriteLine($"Compare date1 {date1:U}, date2 {date2:U}: {dateOnly:U}");
var pdf = renderer.RenderHtmlAsPdf(content);
pdf.SaveAs("outputDate.pdf"); // Saves PDF
}
public static string CompareDatesWithCompare(DateTime date1, DateTime date2)
{
int result = date1.CompareTo(date2);
string resultString;
if (result < 0)
{
resultString = "date1 is earlier than date2.";
Console.WriteLine(resultString);
}
else if (result > 0)
{
resultString = "date1 is later than date2.";
Console.WriteLine(resultString);
}
else
{
resultString = "date1 is equal to date2.";
Console.WriteLine(resultString);
}
return resultString;
}
public static string CompareDates(DateTime date1, DateTime date2)
{
string result;
if (CheckLessor(date1, date2))
{
result = "date1 is earlier than date2.";
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
else if (CheckGreater(date1, date2))
{
result = "date1 is later than date2.";
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
else
{
result = "date1 is equal to date2.";
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
return result;
}
public static bool CheckGreater(DateTime date1, DateTime date2)
{
return date1 > date2;
}
public static bool CheckLessor(DateTime date1, DateTime date2)
{
return date1 < date2;
}
}Friend Class Program
Shared Sub Main()
Console.WriteLine("-----------Iron Software-------------")
Dim renderer = New ChromePdfRenderer() ' var pattern
Dim content = " <h1> Iron Software is Awesome </h1> Made with IronPDF!"
content &= "<h2>Demo Datetime Objects in C#</h2>"
' Current date and time
content &= "<h3>Current date and time</h3>"
Dim currentDateTime As DateTime = DateTime.Now
content &= $"<p>Current date and time: {currentDateTime:U}</p>"
Console.WriteLine($"Current date and time: {currentDateTime:U}")
' Specific date and time
content &= "<h3>Specific date and time</h3>"
Dim specificDateTime As New DateTime(2024, 3, 16, 10, 30, 0)
content &= $"<p>Specific date and time: {specificDateTime:U}</p>"
Console.WriteLine($"Specific date and time: {specificDateTime:U}")
' Date only
content &= "<h3>Date Only</h3>"
Dim dateOnly As DateTime = DateTime.Today
content &= $"<p>Date only: {dateOnly:U}</p>"
Console.WriteLine($"Date only: {dateOnly:U}")
' Date and time in UTC
content &= "<h3>Date and time in UTC</h3>"
Dim utcDateTime As DateTime = DateTime.UtcNow
content &= $"<p>Date only: {dateOnly:U}</p>"
Console.WriteLine($"Date only: {dateOnly:U}")
'Compare dates with Operators
content &= "<h3>Compare dates with Operators</h3>"
Dim date1 As DateTime = DateTime.Now
Dim date2 As DateTime = DateTime.Now.AddDays(1)
content &= $"<p>Compare date1 {date1:d}, date2 {date2:d}: {CompareDates(date1, date2)}</p>"
Console.WriteLine($"Compare date1 {date1:U}, date2 {date2:U}: {dateOnly:U}")
'Compare dates with Compare Method
content &= "<h3>Compare dates with Compare Method</h3>"
content &= $"<p>Compare date1 {date1:d}, date2 {date2:d}: {CompareDatesWithCompare(date1, date2)}</p>"
Console.WriteLine($"Compare date1 {date1:U}, date2 {date2:U}: {dateOnly:U}")
Dim pdf = renderer.RenderHtmlAsPdf(content)
pdf.SaveAs("outputDate.pdf") ' Saves PDF
End Sub
Public Shared Function CompareDatesWithCompare(ByVal date1 As DateTime, ByVal date2 As DateTime) As String
Dim result As Integer = date1.CompareTo(date2)
Dim resultString As String
If result < 0 Then
resultString = "date1 is earlier than date2."
Console.WriteLine(resultString)
ElseIf result > 0 Then
resultString = "date1 is later than date2."
Console.WriteLine(resultString)
Else
resultString = "date1 is equal to date2."
Console.WriteLine(resultString)
End If
Return resultString
End Function
Public Shared Function CompareDates(ByVal date1 As DateTime, ByVal date2 As DateTime) As String
Dim result As String
If CheckLessor(date1, date2) Then
result = "date1 is earlier than date2."
Console.WriteLine(result)
ElseIf CheckGreater(date1, date2) Then
result = "date1 is later than date2."
Console.WriteLine(result)
Else
result = "date1 is equal to date2."
Console.WriteLine(result)
End If
Return result
End Function
Public Shared Function CheckGreater(ByVal date1 As DateTime, ByVal date2 As DateTime) As Boolean
Return date1 > date2
End Function
Public Shared Function CheckLessor(ByVal date1 As DateTime, ByVal date2 As DateTime) As Boolean
Return date1 < date2
End Function
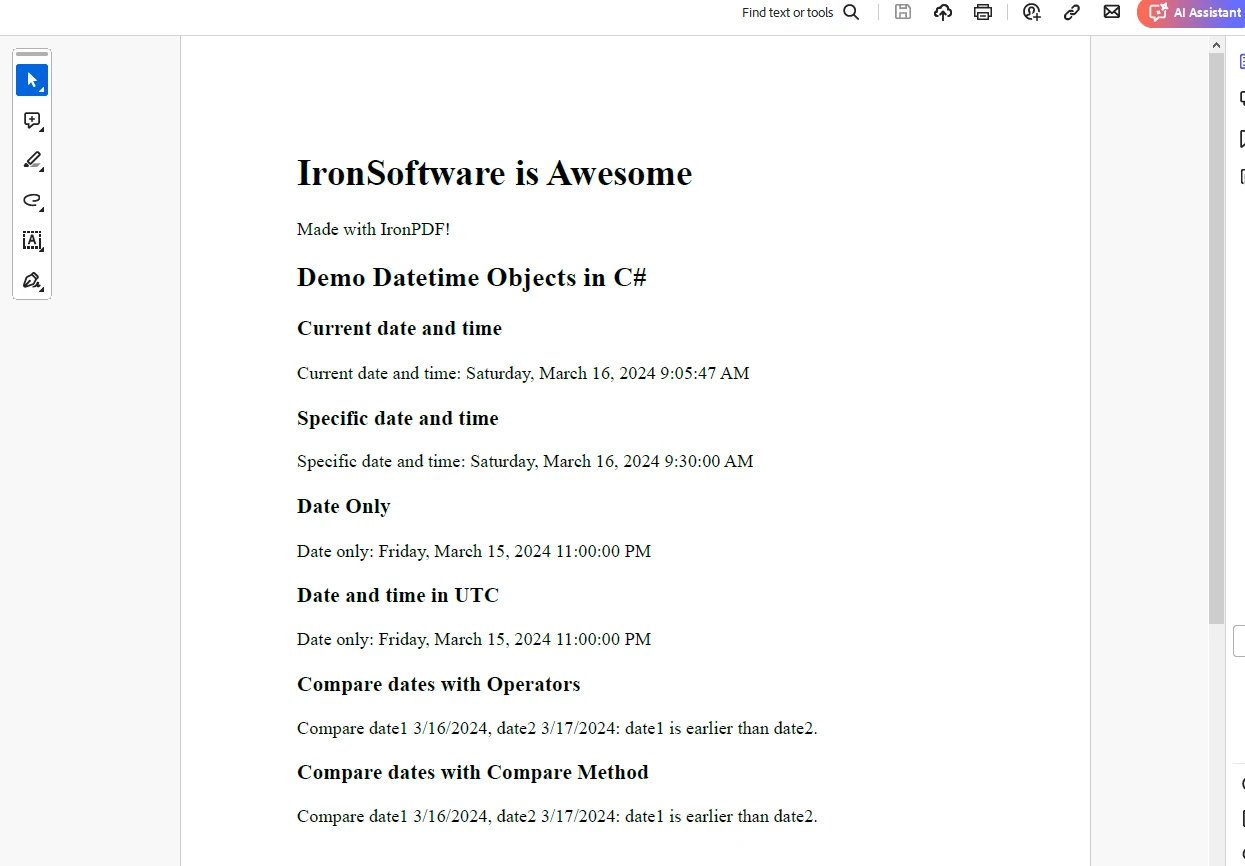
End ClassThe following output shows the PDF generated with DateTime objects:
IronPDF. Provide an Email ID to generate a license key that will be then delivered to the email you provided.
"IronPDF.LicenseKey": "<Your Key>""IronPDF.LicenseKey": "<Your Key>"'INSTANT VB TODO TASK: The following line uses invalid syntax:
'"IronPDF.LicenseKey": "<Your Key>"Place the License key in the AppSettings.Json file.
DateTime objects in C# provide a powerful way to work with dates and times in .NET applications. They offer a wide range of functionalities for creating, manipulating, formatting, and comparing date and time values. Understanding how to effectively use DateTime objects is essential for building reliable and accurate date and time functionalities in C# applications.
By leveraging the capabilities of DateTime objects, developers can ensure that their applications handle dates and times correctly, regardless of the specific requirements or scenarios they encounter.
Whether it's calculating durations, scheduling tasks, or displaying dates and times to users, DateTime objects play a crucial role in many aspects of C# programming related to date and time management.